Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e183024. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.183024.
Abstract
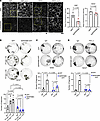
Impairment of desmosomal cell-cell adhesion leads to life-threatening diseases, such as the autoimmune skin-blistering disorder pemphigus vulgaris (PV). Disease management strategies that stabilize intercellular adhesion, in addition to the existing immunosuppression therapies, may result in improved clinical outcomes. Previous findings showed that the serine protease inhibitor SERPINB5 promotes intercellular adhesion by binding to and regulating the localization of the desmosomal adapter molecule desmoplakin (DSP) at the plasma membrane. We here show that SERPINB5 overexpression prevents PV-IgG–mediated loss of cell-cell adhesion and DSP dissociation from the cell membrane. We mechanistically demonstrate that SERPINB5 loss deregulates TGF-β signaling, a pathway known to destabilize DSP in keratinocytes. TGF-β signaling was also activated in skin biopsies of patients with PV and keratinocytes treated with PV autoantibodies, suggesting a contribution to disease. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling ameliorated PV-IgG–mediated loss of cell-cell adhesion, increased DSP membrane expression, and prevented PV-IgG–induced blister formation in a human ex vivo skin model. Together, SERPINB5 modulates DSP and intercellular adhesion through the regulation of TGF-β signaling. Further, TGF-β signaling was identified as a potential target for pemphigus treatment.
Authors
Maitreyi Rathod, Mariam Petrosyan, Aude Zimmermann, Maike Märker, Tobias Gosau, Henriette Franz, Tomás Cunha, Dario Didona, Michael Hertl, Enno Schmidt, Volker Spindler
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e193054. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.193054.
Abstract
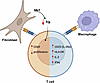
In the rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovium, resident fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) express MHC class II molecules (HLA-D) but lack the costimulatory signals typically required for T cell activation. Here, we demonstrate that antigen presentation by FLS induces a distinct T cell activation state characterized by high CD69 yet reduced CD25 and HLA-DR expression, suppressed proliferation, and decreased effector cytokine production compared with professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as macrophages. FLS were also capable of suppressing macrophage-induced T cell activation, underscoring their dominant immunomodulatory role in the synovial microenvironment. Mechanistically, we identify indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase–mediated (IDO1-mediated) tryptophan depletion as the primary driver of FLS-induced T cell hyporesponsiveness. Spatial transcriptomics revealed colocalization of IDO1 and CD69 within ectopic lymphoid structures in RA synovium, further supporting the in vivo relevance of this pathway. These findings provide the groundwork for positioning FLS as critical T cell regulators in RA and highlight the importance of preserving their immunosuppressive properties when therapeutically targeting pathogenic FLS functions.
Authors
Melissa R. Romoff, Preethi K. Periyakoil, Edward F. DiCarlo, Daniel Ramirez, Susan M. Goodman, Christina S. Leslie, Alexander Y. Rudensky, Laura T. Donlin, Melanie H. Smith
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e190227. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.190227.
Abstract
Macular edema (ME) can cause profound vision impairment and occurs in several prevalent retinal diseases, including diabetic retinopathy, choroidal neovascularization, retinal vein occlusion, and uveitis. Retinal edema typically results from dysfunction of the blood-retina barrier (BRB), which is associated with increased retinal expression of complement components. It is unclear whether the classical complement pathway has detrimental or protective roles in the context of BRB dysfunction. Here, we characterized Tspan12-KODBM (disrupted BRB maintenance) mice, a mouse model of cystoid edema generated by genetically and pharmacologically manipulating β-catenin–dependent norrin/frizzled-4 (FZD4) signaling. We assessed BRB function, cystoid edema, electroretinogram, and microglia activation outcomes in an aging study with WT, C1qa-KO, Tspan12-KODBM, and Tspan12-KODBM; C1qa-KO compound mutant mice. Phenotypic analyses and cell-based experiments indicated that C1QA contributes to maintaining basal β-catenin–dependent signaling and that the absence of C1QA exacerbates BRB dysfunction, cystoid edema, and neuroinflammation in Tspan12-KODBM; C1qa-KO compound mutant mice. Activation of β-catenin–dependent signaling by an anti-FZD4 and anti-LRP5 agonistic antibody modality achieved complete resolution of cystoid edema. This study shows that reducing or enhancing norrin/FZD4 signaling can increase or decrease cystoid edema, respectively, underscoring its potential as a therapeutic target in ME. Furthermore, this study provides insights into the contribution of C1QA to BRB maintenance.
Authors
Lingling Zhang, Jacklyn Levey, Md. Abedin, Ha-Neul Jo, Emmanuel Odame, Miranda Howe, Kaia L. Douglas, Elise Thoreen, Scott W. McPherson, Heidi Roehrich, Somasekar Seshagiri, Stephane Angers, Zhe Chen, Harald J. Junge
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e189850. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.189850.
Abstract
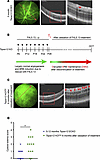
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a prevalent arrhythmia with known detriments such as heart failure, stroke, and cognitive decline even in patients without prior stroke. The mechanisms by which AF leads to cognitive dysfunction are yet unknown, and there is a lack of animal models to study this disease process. We previously developed a murine model of spontaneous and prolonged episodes of AF, a double transgenic mouse model with cardiac-specific expression of a gain-of-function mutant voltage-gated sodium channel (DTG-AF mice). Herein, we show, for the first time to our knowledge, a murine model of AF without any cerebral infarcts exhibiting cognitive dysfunction, including impaired visual learning and cognitive flexibility on touch screen testing. Mesenteric resistance arterial function of DTG-AF mice showed significant loss of myogenic tone, increased wall thickness and distensibility, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Brain pial arteries also showed increased wall thickness and mitochondrial enlargement. Furthermore, DTG-AF mice have decreased brain perfusion on laser speckle contrast imaging compared with controls. Cumulatively, these findings demonstrate that AF leads to vascular structural and functional alterations necessary for dynamic cerebral autoregulation, resulting in increased cerebral stress and cognitive dysfunction. Expression of mitochondrial catalase (mCAT) to reduce mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) was sufficient to prevent vascular dysfunction due to AF, restore perfusion, and improve cognitive flexibility.
Authors
Pavithran Guttipatti, Ruiping Ji, Najla Saadallah, Uma Mahesh R. Avula, Deniz Z. Sonmez, Albert Fang, Eric Li, Amar D. Desai, Samantha Parsons, Parmanand Dasrat, Christine Sison, Yanping Sun, Chris N. Goulbourne, Steven R. Reiken, Elaine Y. Wan
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e195385. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.195385.
Abstract
IDH1/2 mutations (IDHmut) increase methylation of DNA and histones in gliomas. IDHmut inhibitors are effective against low-grade IDHmut gliomas, but new strategies against high-grade IDHmut gliomas are needed. Although histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) are ineffective against IDHwt glioblastoma (GBM), their potential in IDHmut gliomas has not been extensively studied. We previously established that IDHmut gliomas are more sensitive to HDACi than IDHwt GBM. Here we show that IDHmut is associated with greater sensitivity to HDACi only in glioma, not in IDHmut chondrosarcoma or cholangiocarcinoma. While HDACi induced more histone acetylation and gene regulation in IDHmut glioma than in IDHwt GBM, such acetylation was mostly within gene deserts, whereas IDHmut glioma promoters paradoxically lost histone acetylation. Two mediators of HDACi resistance, YAP and TAZ, were methylated and suppressed in IDHmut gliomas but not in other IDHmut cancers. Inducing YAP or TAZ expression in IDHmut gliomas conferred resistance to HDACi. Finally, belinostat extended in vivo survival only in IDHmut glioma models, not in IDHmut GBM models. Our findings provide a mechanistic rationale for further studies of HDACi in patients with IDHmut glioma, as well as the potential use of YAP/TAZ as a biomarker of HDACi sensitivity in cancers.
Authors
Thomas K. Sears, Matthew McCord, Wenxia Wang, Alicia Steffens, Kathleen McCortney, Rahul Chaliparambil, Jann N. Sarkaria, Craig M. Horbinski
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e191538. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.191538.
Abstract
Intestinal epithelial barrier integrity is essential for human health, and its disruption induces and exacerbates intestinal inflammatory disorders. While the epithelial cytoskeleton is critical for maintaining gut barrier-integrity, the role of septins — a family of GTP-binding, cytoskeletal proteins — is largely unknown. This highlights an important knowledge gap, as dysfunction of septins, and specifically septin 9 (SEPT9), is associated with intestinal pathologies. We determined that SEPT9 localizes to the apical junctions of intestinal epithelial cells (IECs), overlapping with both tight and adherens junctions. IEC-specific ablation of SEPT9 in mice resulted in leaky gut, due to mislocalization of junctional proteins, and increased susceptibility to experimental colitis. Consistently, SEPT9 expression was significantly reduced in intestinal mucosa of patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Using affinity-purification mass spectrometry, super-resolution imaging, and genetic KO, we determined that SEPT9 interacts with and is necessary to recruit nonmuscle myosin IIC (NMIIC) to the IEC perijunctional actomyosin belt. Loss of NMIIC also caused IEC barrier disruption. In summary, SEPT9 regulates intestinal barrier integrity by supporting the assembly of tight and adherens junctions through NMIIC recruitment to the actomyosin belt. The septin cytoskeleton safeguards the intestinal mucosa during acute inflammation, and its disruption in IBD suggests a loss of this protective function.
Authors
Nayden G. Naydenov, Gaizun Hu, Dominik Robak, Atif Zafar, Khosiyat Makhmudova, Susana Lechuga, Yuta Ohno, Naseer Sangwan, Saikat Bandyopadhyay, Ryan Musich, Erin Jeffery, Lei Sun, Armando Marino-Melendez, Florian Rieder, Gloria Sheynkman, Andrei I. Ivanov, Seham Ebrahim
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e189286. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.189286.
Abstract
The MTM1 gene encodes myotubularin (MTM1), a phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate [PI(3)P] lipid phosphatase. Loss-of-function mutations in MTM1 cause X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM), a severe congenital myopathy with no available cure and a poorly understood pathomechanism. The importance of MTM1 enzymatic activity and its PI(3)P substrate in physiology under normal conditions and in XLMTM is unclear. We generated the Mtm1-KI C375S mice in which the endogenous MTM1 was converted to a phosphatase-dead protein. Mutant mice survived a median of 12 weeks and demonstrated progressively impaired motor skills. Observed muscle hypotrophy and reduced force production compared with their WT littermates (~3.9-fold reduction in absolute maximal force) were responsible for these severe phenotypes. A significantly higher level of PI(3)P was found in the muscle of Mtm1-KI C375S mice. Muscle histology and molecular characterization revealed XLMTM hallmarks, with (a) alteration of the mTOR and autophagy pathways correlating with muscle hypotrophy and (b) abnormal myofiber intracellular organization correlating with impaired muscle force. Overall, this study reveals the importance of MTM1 phosphatase activity and related PI(3)P substrate for postnatal muscle maintenance, and it highlights the significance of MTM1 phosphatase activity in the development of X-linked myotubular myopathy.
Authors
Foteini Moschovaki-Filippidou, Christine Kretz, David Reiss, Gaëtan Chicanne, Bernard Payrastre, Jocelyn Laporte
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e194581. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.194581.
Abstract
Laminin-α2–related congenital muscular dystrophy (LAMA2-CMD) is a severe neuromuscular disorder caused by mutations in the LAMA2 gene, leading to loss of heterotrimers laminin-211/221, key components of the skeletal muscle extracellular matrix. Their absence disrupts adhesion between the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix, resulting in progressive muscle wasting. Laminin-211/221 interacts with adhesion complexes such as the dystrophin/utrophin glycoprotein complex and α7β1-integrin. However, the regulatory mechanisms of these laminin-binding complexes and the broader role of laminin’s influence on the formation of the macromolecular network in skeletal muscle remain unclear. We previously demonstrated that delivering mouse laminin-111 to the dyW–/– mouse model of LAMA2-CMD prevented disease progression, improved strength, and extended survival. We hypothesize that laminin-111, the embryonic laminin isoform, restores key adhesion-signaling networks. Using spatial proteomics on patient and mouse muscle, we identified loss of essential signaling components: heat shock proteins 27 and 70, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and glucose transporter 1 in laminin-α2–deficient muscle. Treatment with recombinant human laminin-111 (rhLAM-111) restored protein localization, reduced ROS, and promoted glycolytic, prosurvival signaling. These findings highlight laminin’s role in maintaining muscle homeostasis and metabolism and support the therapeutic potential of rhLAM-111 for treating LAMA2-CMD by restoring adhesion and intracellular signaling in dystrophic muscle.
Authors
Hailey J. Hermann, Ryan D. Wuebbles, Marisela Dagda, Axel Muñoz, Lauren L. Parker, Paula C. Guzman, Lola T. Byrne, Steven A. Moore, Dean J. Burkin
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e194188. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.194188.
A multiomics analysis identifies retinol metabolism in fibroblasts as a key pathway in wound healing
Abstract
Impaired wound healing poses a major and increasingly frequent health problem. Among the key players in the healing process are fibroblasts, but their metabolic profile in healing wounds is largely unknown. Using a combination of transcriptomics, targeted proteomics, and metabolomics, we identified retinol metabolism as a top regulated pathway in wound fibroblasts. This is functionally relevant, since even a mild retinol deficiency caused a delay in wound closure and reepithelialization, which mainly resulted from misdirected keratinocyte migration on the new granulation tissue. Quantitative proteomics identified integrin subunit α11 as a less abundant protein in wounds of mice subjected to a retinol-deficient diet. Reduced levels of this fibroblast-specific protein likely altered the granulation tissue matrix, which in turn affected reepithelialization. These results provide a comprehensive overview of the transcriptome, proteome, and metabolome of wound fibroblasts and identify retinol metabolism in fibroblasts as a key regulator of tissue repair.
Authors
Till Wüstemann, Elizabeta Madzharova, Mateusz S. Wietecha, Norbert B. Ghyselinck, Marcus Höring, Gerhard Liebisch, Nicola Zamboni, Ulrich auf dem Keller, Sabine Werner
Citation Information: JCI Insight. 2025;10(22):e191697. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.191697.
Abstract
Genetic diseases such as ion channelopathies substantially burden human health. Existing treatments are limited and not genotype specific. Here, we report a 2-step high-throughput approach to rapidly identify drug candidates for repurposing as genotype-specific therapy. We first screened 1,680 medicines using a thallium-flux trafficking assay against Kv11.1 gene variants causing long QT syndrome (LQTS), an ion channelopathy associated with fatal cardiac arrhythmia. We identified evacetrapib as a suitable drug candidate that improves membrane trafficking and activates channels. We then used deep mutational scanning to prospectively identify all Kv11.1 missense variants in an LQTS hotspot region responsive to treatment with evacetrapib. Combining high-throughput drug screens with deep mutational scanning establishes a paradigm for mutation-specific drug discovery translatable to personalized treatment of carriers with rare genetic disorders.
Authors
Christian L. Egly, Alex Shen, Tri Q. Do, Carlos Tellet Cabiya, Paxton A. Ritschel, Suah Woo, Matthew Ku, Brian P. Delisle, Brett M. Kroncke, Björn C. Knollmann
No posts were found with this tag.