Inflammation
Abstract
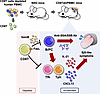
Clonal haematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) is the expansion of blood stem cells and progeny after somatic mutation. CHIP associates with increased cardiovascular disease (CVD) with inflammation from macrophages a proposed common effector. However, mouse CHIP studies are discordant for clonal expansion and inflammation. Similarly, directionality of association between CHIP and CVD remains debated. We investigated effects of three CHIP mutations on macrophage cytokines, clonal expansion and atherosclerosis in parallel. We find that Tet2 and Dnmt3a mutations increase cytokines and inflammasome activation in Tet2 but decrease in Dnmt3a. However, Jak2 mutant macrophages produced equivalent cytokine as wild-type. In mice, Tet2 mutants clonally expanded, but Dnmt3a and Jak2 mutants didn’t. Expansion was unaffected by systemic inflammation, while hyperlipidemia expanded Tet2-/- cells, but not mono-allelic mutants. Similarly, human Mendelian randomisation showed no effect of serum cytokines or CVD on CHIP risk. Experimental atherosclerosis was increased in females with Tet2 and males with Jak2, but unchanged with Dnmt3a mutations. Together, common CHIP mutations have disparate effects on macrophage cytokines and clonal expansion, and sex-dependent effects on atherogenesis, suggesting a common mechanism across CHIP is unlikely. Thus, CHIP mutations differ in pathophysiology and clinical sequalae across sexes and should be treated as different entities.
Authors
Paul R. Carter, Lauren Kitt, Amanda Rodgers, Nichola Figg, Ang Zhou, Chengrui Zhu, Ziyang Wang, Peter Libby, Stephen Burgess, George S. Vassiliou, Murray CH. Clarke
Abstract
BACKGROUND Icotrokinra is the first and only targeted oral peptide that selectively binds the IL-23 receptor with high affinity to precisely inhibit IL-23 signaling. Icotrokinra demonstrated high rates of complete skin clearance and durable disease control in the phase IIb trial, FRONTIER-1, and its long-term extension, FRONTIER-2, in participants with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. This study evaluated systemic and skin pharmacodynamic response of icotrokinra and its relationship to clinical response in FRONTIER participants.METHODS FRONTIER-1 participants received icotrokinra or placebo for 16 weeks. FRONTIER-2 followed participants for up to 1 year of treatment; placebo participants transitioned to icotrokinra after week 16. Systemic pharmacodynamic changes were assessed in serum through week 52. Skin pharmacodynamic changes were assessed using transcriptomic analysis of skin biopsies and protein quantification in tape-strip samples through week 16.RESULTS Icotrokinra dose-dependently reduced serum levels of the IL-23/IL-17 axis and psoriasis disease biomarkers through week 52, with maximal reductions observed with the highest 100 mg twice-daily dose. Proteomic analyses showed icotrokinra selectively blocked IL-23–driven inflammation without broader impacts on circulating proteins, including serum IL-23 levels. Sixteen weeks of icotrokinra, but not placebo, reduced expression of psoriasis-associated genes in lesional skin. Icotrokinra treatment also reduced psoriasis-relevant proteins in week 16 lesional skin tape-strips to levels comparable to nonlesional samples.CONCLUSION Icotrokinra induced a dose-dependent pharmacodynamic response, with early (week 4) and sustained (week 52) reductions in biomarkers of IL-23 pathway activation and psoriasis disease severity, which correlated with clinical response.TRIAL REGISTRATION ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05223868, NCT05364554.FUNDING Johnson & Johnson.
Authors
David Strawn, James G. Krueger, Robert Bissonnette, Kilian Eyerich, Laura K. Ferris, Amy S. Paller, Andreas Pinter, Dylan Richards, Elizabeth Y. Chen, Kate Paget, Daniel Horowitz, Roohid Parast, Joshua J. Rusbuldt, Jocelyn Sendecki, Sunita Bhagat, Lynn P. Tomsho, Ching-Heng Chou, Marta E. Polak, Brice E. Keyes, Emily Bozenhardt, Yuan Xiong, Wangda Zhou, Cynthia DeKlotz, Paul Newbold, Dawn M. Waterworth, Megan Miller, Takayuki Ota, Ya-Wen Yang, Monica W.L. Leung, Lloyd S. Miller, Carolyn A. Cuff, Bradford McRae, Darren Ruane, Arun K. Kannan
Abstract
BACKGROUND Platelets are increasingly recognized as active participants in immune signaling and systemic inflammation. Upon activation, platelets form monocyte platelet aggregates (MPA) representing the crossroads of thrombosis and inflammation. We hypothesized that platelet transcriptomics could capture this thromboinflammatory axis and identify individuals at elevated cardiovascular risk.METHODS: MPA levels, defined as CD14+CD61+ cells, were measured using flow cytometry at 2 time points, 4 weeks apart, in healthy individuals Platelets were isolated and sequenced. Individuals were categorized as MPAhi or MPAlo based on consistently high or low MPA levels across time points.RESULTS Among 149 participants (median age 52 years, 57% female, 50% non-White), MPAhi individuals exhibited increased expression of platelet activation markers P-selectin (P < 0.001), PAC-1 (P = 0.021), and CD40L (P < 0.001) and enriched immune signaling pathways. Informed by MPA levels and derived from the platelet transcriptome, we developed a 42-gene thromboinflammation platelet signature (TIPS), which correlated with MPA levels in multiple cohorts and was reproducible over time. TIPS was elevated in patients with COVID-19 (P = 0.0002) and myocardial infarction (Padj = 0.008), and as in predicted future cardiovascular events in patients who underwent lower extremity revascularization after a median follow-up of 18 months (adjusted for age, sex, race, and ethnicity [adjHR] 1.55, P = 0.006). Notably, TIPS was modifiable by ticagrelor (P = 0.002) but not aspirin.CONCLUSION These findings establish MPA as a biomarker of thromboinflammation and introduce TIPS, a platelet RNA signature, that captures thromboinflammation and provides a promising tool for cardiovascular risk stratification and a potential therapeutic target.TRIAL REGISTRATION NCT04369664FUNDING NIH R35HL144993, NIH R01HL139909, and AHA 16SFRN2873002 to JSB, DFG Walter-Benjamin-Programme 537070747 to AB.
Authors
Antonia Beitzen-Heineke, Matthew A. Muller, Yuhe Xia, Elliot Luttrell-Williams, Florencia Schlamp, Deepak Voora, Kelly V. Ruggles, Michael S. Garshick, Tessa J. Barrett, Jeffrey S. Berger
Abstract
Oral lichen planus (OLP) is a recalcitrant inflammatory disease with potential for malignant transformation, involving a cytotoxic CD8+ T cells-mediated basal keratinocyte apoptosis. However, it lacks an appropriate mouse model for study. Here we developed an OLP-like mouse model using topical oxazolone to induce a delayed-type hypersensitivity-mediated oral lichenoid reaction. Histological and ultrastructural analysis confirmed hallmark pathological features of OLP, including band-like CD8+ T cell infiltration and basal cell damage, and the presence of Civatte bodies. Comparative transcriptomic analysis revealed significant similarity between RNA-seq profiles of the mouse model and human OLP lesions, highlighting shared upregulated genes and enriched pathways, particularly those related to IFN-γ signaling and cytotoxic T cell activity. Functional studies demonstrated that the OLP phenotype depended on IFN-γ, with local priming by IFN-γ intensifying the disease through upregulation of major histocompatibility complex class I. Additionally, the absence of Langerhans cells exacerbated disease severity in vivo. Therapeutic evaluation showed that the JAK inhibitors baricitinib and ruxolitinib effectively reduced disease burden and provided mechanistic insights. In conclusion, this OLP-like mouse model recapitulates key immunopathological and transcriptomic features of human OLP, offering a robust platform for dissecting disease mechanisms and evaluating novel therapeutic strategies.
Authors
Zhenlai Zhu, Tinglan Yang, Peng Peng, Kang Li, Wen Qin, Chen Zhang, Shuyan Wang, Yuanyuan Wang, Minghui Wei, Erle Dang, Meng Fu, Hao Guo, Wen Yin, Shuai Shao, Qing Liu
Abstract
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a major mechanism of acute kidney injury (AKI), and increased circulating interleukin 6 (IL-6) is associated with systemic inflammation and death due to sepsis. We tested whether kidney mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) contributes to IL-6 release in sepsis-associated AKI via Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9). In a murine model of sepsis via cecal ligation and puncture (CLP), we used next-generation sequencing of plasma mtDNA to inform the design of optimal target sequences for quantification by droplet digital PCR, and to identify single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to infer tissue origin. We found significantly higher concentrations of plasma mtDNA after CLP versus shams and that plasma mtDNA SNPs matched kidney SNPs more than other organs. Kidney mtDNA contributed directly to IL-6 and mtDNA release from dendritic cells in vitro and kidney mitochondria solution led to higher IL-6 concentrations in vivo. IL-6 release was mitigated by a TLR9 inhibitor. Finally, plasma mtDNA was significantly higher in septic patients with AKI compared with those without AKI and correlated significantly with plasma IL-6. We conclude that AKI contributes to increased circulating IL-6 in sepsis via mtDNA release. Targeting kidney mitochondria and mtDNA release are potential translational avenues to decrease mortality from sepsis-associated AKI.
Authors
Avnee J. Kumar, Katharine Epler, Jing Wang, Alice Shen, Negin Samandari, Mark L. Rolfsen, Laura A. Barnes, Gerald S. Shadel, Alexandra G. Moyzis, Alva G. Sainz, Karlen Ulubabyan, Kefeng Li, Kristen Jepsen, Xinrui Li, Mark M. Fuster, Roger G. Spragg, Roman Sasik, Volker Vallon, Helen Goodluck, Joachim H. Ix, Prabhleen Singh, Mark L. Hepokoski
Abstract
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection. During early sepsis, kinins are released and bind to B1 (BDKRB1) and B2 (BDKRB2) bradykinin receptors, but the involvement of these receptors in sepsis remains incompletely understood. This study demonstrated that the genetic deletion of Bdkrb2 had no significant impact on sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) compared to wild-type (WT) mice. In contrast, Bdkrb1−/− mice subjected to CLP exhibited decreased lethality and bacterial load, associated with an increased influx of neutrophils into the peritoneal cavity, compared with WT mice. Neutrophils from CLP-Bdkrb1−/− mice partially restored CXCR2 expression and reduced the upregulation of P110γ observed in WT CLP neutrophils. Pharmacologic inhibition of BDKRB1 combined with imipenem treatment substantially improved survival compared with antibiotic therapy alone. In human neutrophils, stimulation with LPS led to the upregulation of BDKRB1 expression, and antagonism of BDKRB1 restored neutrophil migration in response to CXCL8. These findings identify BDKRB1 as an important modulator of neutrophil dysfunction in sepsis and a promising therapeutic target whose inhibition improves bacterial clearance, restores neutrophil migration, and increases the efficacy of antibiotic treatment.
Authors
Raquel Duque do Nascimento Arifa, Carolina Braga Resende Mascarenhas, Lívia Caroline Resende Rossi, Maria Eduarda Freitas Silva, Larissa M. Lucas, João Paulo Pezzini Barbosa, Daiane Boff, Brenda Gonçalves Resende, Lívia Duarte Tavares, Alesandra Corte Reis, Vanessa Pinho, Flavio Almeida Amaral, Caio Tavares Fagundes, Cristiano Xavier Lima, Mauro Martins Teixeira, Daniele G Souza
Abstract
Peripheral helper T (Tph) and follicular helper T (Tfh) cells are key regulators of B cell differentiation and antibody production, making them promising targets for autoimmune disease treatment. However, their differentiation mechanisms differ significantly between humans and mice, limiting drug validation in mouse models. Here, we present a simple and effective method for in vivo proliferation of human Tph/Tfh and B cells. We discovered that after depleting CD8+ T cells of human peripheral blood mononuclear cell–transferred immunodeficient mice (CD8TΔhPBMC mice), human Tph/Tfh cells and B cells proliferated markedly in the spleen compared with those in human PBMC–transferred immunodeficient mice (hPBMC mice). Transcriptome analysis confirmed proliferating cells’ close resemblance to human Tph/Tfh cells. Furthermore, multicolor flow cytometry revealed CXCL13+ Tph cells infiltrating Sjögren’s syndrome–associated (SjS-associated) organs, such as salivary glands. Single-cell RNA sequencing identified IL-21+CXCL13+IFN-γ+ICOS+TIGIT+GPR56+ Tph cells in the salivary glands. These findings are consistent with reduced saliva volume and elevated SjS markers, such as anti-SSA antibody, in these mice, which were both ameliorated by immunosuppressants. In vitro, CD8+ T cells from hPBMC mice induced B cell apoptosis and inhibited Tph/Tfh differentiation. This model advances understanding of human Tph/Tfh cell biology and offers a valuable platform for studying SjS and therapeutic targets.
Authors
Mariam Piruzyan, Sota Fujimori, Ryota Sato, Yuki Imura, Sachiko Mochiduki, Kana Takemoto, Akiko Nishidate, Yuzo Koda
Abstract
Processes that promote white adipocyte inflammatory function remain incompletely defined. Here, we demonstrated that type I interferon–dependent (IFN-I–dependent) skewing of adipocyte glycolysis, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) utilization, and pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 (PKM2) function may contribute to increased systemic and tissue inflammation and disease severity in obesity. Notably, chemical and/or genetic inhibition of glycolysis, the NAD+ salvage pathway, or PKM2 restricted IFN-I–dependent increase in adipocyte inflammatory cytokine production. Further, genetic or small molecule targeting of PKM2 function in vivo was sufficient to reduce systemic and tissue inflammation and metabolic disease severity in obese mice, in an adipocyte PKM2-dependent manner. Further, white adipose tissue of individuals living with obesity and metabolic disease, compared with metabolically healthy individuals with obesity, showed an increase in expression of inflammatory and metabolic genes, while small molecule targeting of PKM2 function contributed to reduced IFN-I–driven inflammatory cytokine production by primary human adipocytes. Together, our findings invoke the IFN-I/PKM2 axis as a potential target for modulating adipocyte dysregulated inflammation.
Authors
Michelle S.M.A. Damen, Pablo C. Alarcon, Calvin C. Chan, Traci E. Stankiewicz, Hak Chung, Keisuke Sawada, Cassidy J. Ulanowicz, John Eom, Jarren R. Oates, Jennifer L. Wayland, Jessica R. Doll, Rajib Mukherjee, Miki Watanabe-Chailland, Lindsey Romick-Rosendale, Sara Szabo, Michael A. Helmrath, Joan Sanchez-Gurmaches, Maria E. Moreno-Fernandez, Senad Divanovic
Abstract
Authors
Zhehao Tan, Gio Wu, Daniela Salgado Figueroa, Paramita Dutta, Zachary Jaeger, Marissa Mazurie, David Schairer, Dawn Eichenfield, Wynnis L. Tom, Lauren Galli, Lawrence Eichenfield, Bob Geng, Brian Hinds, Hal M. Hoffman, Lori Broderick, Ben Croker, Ferhat Ay, Reid Oldenburg
Abstract
Prolonged and dysregulated neutrophilic inflammation causes tissue damage in chronic inflammatory diseases, including antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis (AGN). An increase in glycolysis, supported by enhanced glucose uptake, is a hallmark of hyperneutrophilic inflammation. Neutrophils upregulate glucose transporter 1–mediated (Glut1-mediated) glucose incorporation for renal antimicrobial activities. However, little is known about the role of neutrophil-specific Glut1 function in the pathogenesis of AGN. Using a well-vetted mouse model of AGN, we show that neutrophils upregulate Glut1 expression and function in the nephritic kidney. We demonstrate that Glut1 function in the hematopoietic cells during the early stage of the disease is necessary for kidney pathology. Most importantly, neutrophil-intrinsic Glut1 function is critical for AGN. While neutrophil-specific Glut1 ablation diminished the expression of tissue-damaging effector molecules in both the early and late stages, renal cytokines’ and chemokines’ production were compromised only in the late stage of the disease. Consequently, Glut1 inhibitor treatment ameliorated renal pathology in AGN mice. These data identify a Glut1-driven inflammatory circuit in neutrophils, which is amenable to therapeutic targeting in AGN.
Authors
Hossein Rahimi, Wonseok Choi, Doureradjou Peroumal, Shuxia Wang, Partha S. Biswas
No posts were found with this tag.